Researchers within the UK say the most recent round of the REal-time Assessment of Community Transmission-1 (REACT-1) examine has discovered that the prevalence of an infection with extreme acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) – the agent that causes coronavirus illness 2019 (COVID-19) – has fallen by 50%, in contrast with the previous round carried out in March of this yr (2021).
“We noticed marked reductions in prevalence from March to April and early May 2021 in England reflecting the success of the vaccination program and regardless of easing of restrictions throughout lockdown,” says Steven Riley from Imperial College London and colleagues.
Between the previous round 10 and the most recent round 11, SARS-CoV-2 prevalence fell by two-thirds amongst these aged 55 to 64 years.
On the opposite hand, prevalence charges amongst these aged 25 to 34 years had been comparable between the 2 rounds, regardless of the general discount in prevalence. The group says this will mirror the rise involved charges on this age group, for which vaccine protection was low whereas social mixing restrictions had been eased.
The researchers warn that additional easing of lockdown laws and the presence of the B.1.617.2 lineage that initially emerge in India might result in a rise in prevalence, through which case coverage makers might want to assess the potential influence on hospitalizations and deaths.
A pre-print model of the analysis paper is on the market on the medRxiv* server, whereas the article undergoes peer overview.
Factors that drive dynamics of nationwide an infection patterns
National patterns of SARS-CoV-2 infections are pushed by the diploma of current indoor mixing, vaccine protection, the intrinsic properties of circulating lineages, and prior historical past of an infection.
For instance, India is presently experiencing a big wave of COVID-19 instances and deaths because of the emergence of the B.1.617 variant, following a interval of comparatively elevated ranges of social mixing and low vaccination protection. Meanwhile, the incidence is low in Israel, regardless of social mixing restrictions having been largely relaxed, which is probably going pushed by the results of vaccination.
In England, the speed of infections, hospitalizations and deaths fell this yr through the first two phases of social mixing laws being relaxed on March eighth and April twelfth as half of the “roadmap” for exiting the third nationwide lockdown. During the identical interval, a nationwide vaccination program prioritizing people in line with their danger of dying as soon as contaminated has seen 35.5 million individuals (67.6% of the grownup inhabitants) obtain no less than one dose as of the tenth of May.
Despite the predominant lineage of SARS-CoV-2 throughout this era (B.1.1.7) being extra transmissible than the previous wild-type pressure, the incidence of hospitalizations and deaths has dropped significantly – to solely 2.6% and 0.7%, respectively from the height values in January.
The third step of the roadmap in England befell on the seventeenth of May, with indoor hospitality reopening, the journey ban being lifted, and a few mass occasions being allowed to restart.
Prevalence of nationwide swab-positivity for England estimated utilizing a P-spline for all eleven rounds with central 50% (darkish gray) and 95% (gentle gray) posterior credible intervals. Shown right here just for all the interval of the examine with a Log10 y-axis. Unweighted observations (black dots) and 95% binomial confidence intervals (vertical strains) are additionally proven. Note that the interval between round 7 and round 8 (December) of the mannequin just isn’t included as there have been no information out there to seize the late December peak of the epidemic.
More about round 11 of the REACT-1 examine
Now Riley and colleagues have reported the findings from round 11 of the REACT-1 examine the place self-administered swabs are obtained from a consultant cross-sectional pattern of the inhabitants in England and examined for SARS-CoV-2 an infection by polymerase chain response (PCR).
The outcomes of Round 11, which was carried out between the fifteenth of April and the third of May 2021, had been in contrast with these from round 10 carried out between the eleventh and thirtieth March 2021.
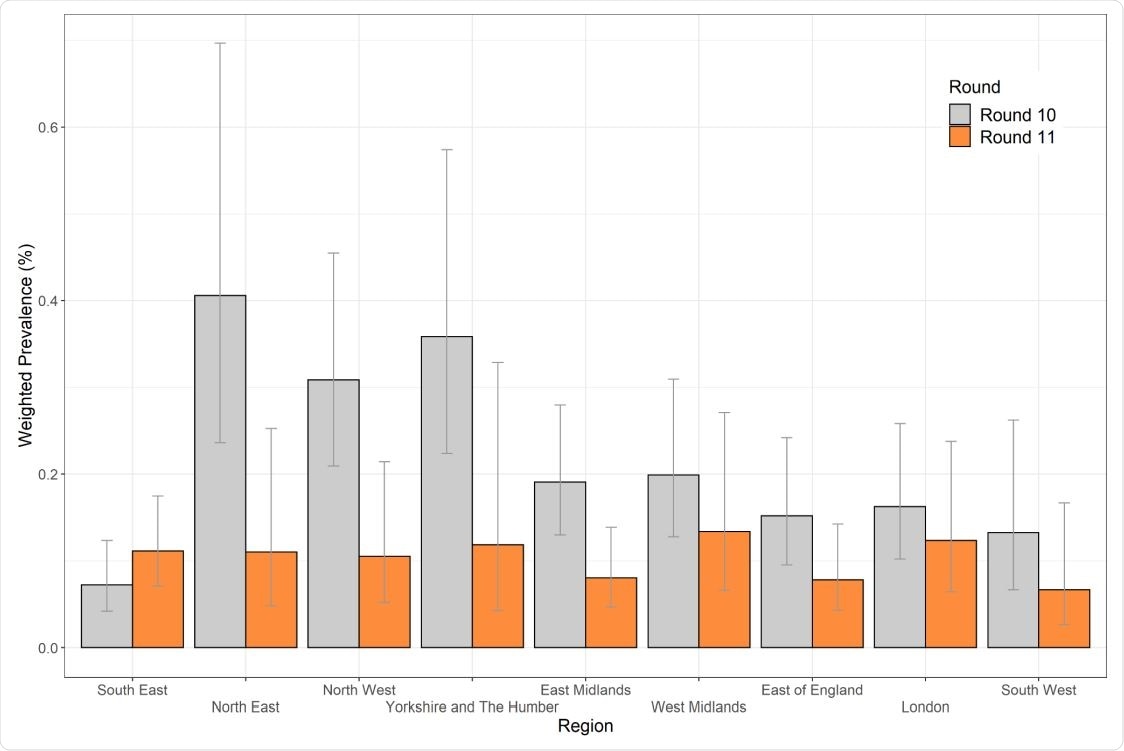
Weighted prevalence of swab-positivity by area for rounds 10 and 11. Bars present 95% confidence intervals.
In the eleventh round, 115 of 127,408 swabs examined PCR-positive for SARS-CoV-2 an infection, giving a prevalence of 0.1%. This in contrast with a prevalence of 0.2% in round 10, thereby representing a 50% lower in round 11 since the previous round.
Among 55 to 64 year-olds, the speed of swab positivity fell by two-thirds from 0.17% in round 10 to 0.06% in round 11, which can mirror the results of the current vaccination roll-out amongst this age group.
By distinction, the speed of swab positivity amongst 25 to 34 year-olds was comparable between round 11 (0.21%) and round 10 (0.18%), regardless of a background of decreasing prevalence.
“This might mirror elevated contact charges, because of the easing of restrictions, on this age group the place there are low ranges of vaccination protection,” says Riley and the group.
Prevalence was greater amongst these of Asian ethnicity
Prevalence in round 11 was greater amongst people of Asian ethnicity than amongst white people, at 0.31% versus 0.09%.
Multivariable logistic regression evaluation estimated that the probability of an infection was 88% greater amongst people of Asian ethnicity, in contrast with white people.
“This means that infections could also be persevering with to unfold extra quickly among the many Asian neighborhood than in different teams within the inhabitants,” writes the group.
Based on the sequence information out there on optimistic samples for which a lineage may very well be recognized, the researchers estimated that 92.3% of infections had been of the B.1.1.7 lineage and that 7.7% had been of the B.1.617.2 lineage.
“Our viral sequencing information point out that the B.1.1.7 lineage stays dominant in England, however that B.1.617.2 can also be circulating in London, in line with studies from Public Health England,” they write.
Vaccination could also be breaking the hyperlink between an infection, hospitalizations and deaths
Riley and colleagues additionally noticed a divergence from the previous shut alignment between an infection incidence measured in REACT-1 and the nationwide price of hospitalizations and deaths recorded by routine surveillance.
The group says the divergence started in January 2021, coinciding with the mass roll-out of vaccination to the aged and most susceptible in society.
The researchers say this means that the vaccination program could also be contributing to decrease charges of extreme outcomes in older age teams, successfully breaking the hyperlink between an infection, hospitalizations and deaths.
“However, there’s potential upwards strain on prevalence from the additional easing of lockdown laws and the presence of the B.1.617.2 lineage,” warns the group.
“If prevalence rises within the coming weeks, policy-makers might want to assess the attainable influence on hospitalizations and deaths. In addition, consideration needs to be given to different well being and financial impacts if elevated ranges of neighborhood transmission happen,” concludes Riley and colleagues.
*Important Notice
medRxiv publishes preliminary scientific studies that aren’t peer-reviewed and, due to this fact, shouldn’t be considered conclusive, information scientific follow/health-related habits, or handled as established data




